AUTONOMY TESTBED FOR MULTI-PURPOSE ORBITING SYSTEMS
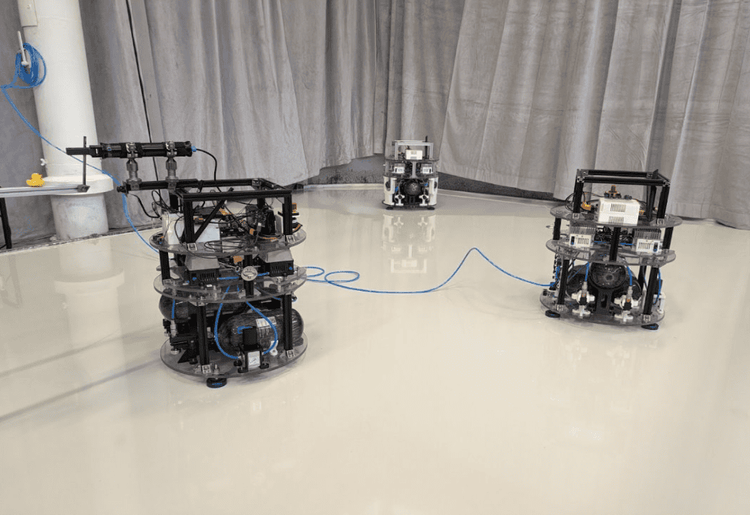
ATMOS is an open-source platform developed at the KTH Space Robotics Laboratory as a research tool for advancing autonomous control of spacecraft. Drawing on extensive experience in modular and open-source technology, it plays a pivotal role in the lab’s mission to innovate autonomy in space systems. Designed for microgravity dynamics simulation, ATMOS is a modular, open-source hardware and software spacecraft-analog platform that is designed to support researchers and industrial hardware development. The platform is equipped with a Pixhawk 6X Mini microcontroller and an Nvidia Jetson Orin NX computer. These enable it to run advanced autonomy tests and integrate other open-source software stacks, such as the Astrobee Flight Software.
ATMOS has been subjected to comprehensive testing in various configurations, from basic modular setups to complex multi-agent operations. The platform navigates using thruster-like compressed air propulsion. However, its modular architecture allows uncomplicated customization to suit different mission objectives, actuation schemes, payload configurations, and environmental conditions. This adaptability, combined with its open-source nature, makes ATMOS a crucial tool for advancing autonomy, control systems, and space robotics research.
ATMOS interfaces over ROS 2 with user-designed software components. The platform is extendable with a wide range of sensors to support research and development in areas such as multi-agent autonomy schemes and microgravity simulations. The KTH Space Robotics Laboratory facilitates multiple ATMOS platforms, a flat floor area, a ground station, low and high-pressure compressors for uninterrupted test sessions, and a Qualisys motion capture system for accurate tracking and benchmarking of developed algorithms.
For more information about the ATMOS platform, please contact the DISCOWER team here.
Read more about ATMOS here.
